
Erlang B
Call Blocking
In an Erlang-B telephone system, N channels are available. New calls are assigned a channel until all channels are full.
Whenever all channels are occupied, a new call is blocked. That is, it is denied a channel. the assumption is that that the calls is lost and that the calling subscriber will not retry again.
This in contrast to an Erlang-C system, in which new calls are queued, until they can be served.
Model
The number of active calls is a Markov process, i.e., at any instant t
the number of active calls statistically only depends on the number of active calls at t - Dt, with very small D t.
New calls arrive according to Poisson process with rate l calls per unit of time. Calls have a (memoryless) exponential duration with mean 1/m. Hence a call terminates with "rate" m and for i calls the rate of termination
of one call is i timesm.
| | 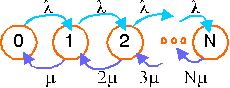 |
Figure: Markov model. The state represents the number of occupied channels in a network with a total of N channels.
|
|
The probability of being in state i, thus with i channels occupied,
can be found from solving the "balance equations" (at equilibrium, the rate of moving into a state should equal the rate of moving out of a state).
One finds
Ai 1
Pi = --- -----------------
i! N Ai
S ----
i=0 i!
where A is the offered traffic expressed in erlang (l/m)
Include animation of an Erlang B process.
PASTA
The "Poisson arrivals see time-averages" (PASTA)-rule says that the probability that a newly arriving call sees a full system equals the time-average probability that the system is in state N.
Thus the blocking probability equals PN.
 Computer Software
Computer Software
PC Windows executable
to compute the amount of traffic that can be carried over Nc channels
with a blocking probability B. The user can set Nc and B.
A JavaScript Calculator is embedded below
Disclaimer: Executable software programmes are provided with no
guarantee whatsoever. See License.
 Erlang B Calculator
Erlang B Calculator
 Example and Exercise
Example and Exercise
A GSM base station uses one carrier of 8 TDMA users.
Find the traffic load (in erlang)
for which the blocking rate is 1%. Answer








 Computer Software
Computer Software Erlang B Calculator
Erlang B Calculator