
 |
JPL's Wireless Communication Reference Website
Chapter: Wireless Channels
|
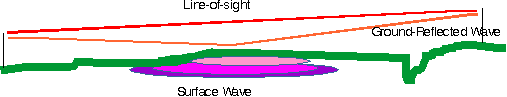
hr+ht
tan(Y) = -----
d
For d >> hr+ht, tan(Y) and sin (Y) approximately equal Y. Meanwhile cos(Y) is about 1.
For a horizontally-polarized wave incident on the surface of a perfectly smooth earth,
![]() ,
,
where er is the relative dielectric constant of the earth, Y is the angle of incidence (between the radio ray and the earth surface) and x = s/(2 p fc e0) with s the conductivity of the ground and e0 the dielectric constant of vacuum. So, x = s/(we0)=18 109s/f.
For vertical polarization
![]()
| Surface | Conductivity s | Relative Dielectric Constant er | |||||||||||||||||
| | | | | |
 Reflection Coefficient Calculator
Reflection Coefficient CalculatorDisclaimer: Executable software programs are provided with no guarantee whatsoever. Some browsers do not support Java applets or JavaScript 1.2. See License.