
 |
JPL's Wireless Communication Reference WebsiteChapter: Wireless Channels
|
|
We initially compute the distribution of received power p.
From this the PDF of received power and the PDF of the amplitude can be derived.
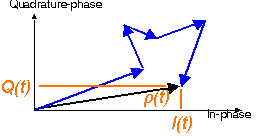
The probability that (x2+y2)/2 < p, with p some power value is
Using the cartesian to polar transform
dxdy = r dr
dq, we get
Thus,
Fp(p) = 1 - exp(- p/s2).This is the (exponential) distribution of received power p. The PDF is found by taking the derivative
The instantaneous power p thus has the above exponential pdf. Conversion between the probability density of amplitude and that of power involves
|fr(r) dr| = |fp(p) dp|and p = r2/2, so dp = rdr. We get:
The pdf of the amplitude is
for r > 0.
|