 |
www.WirelessCommunication.NLChapter: Wireless Propagation Channels
|
![]()
where d_T and d_R are the terminal distances from the knife edge. The diffraction loss, additional to free space loss and expressed in dB, can be closely approximated by
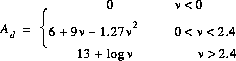
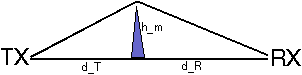
Figure: Path profile model for (single) knife edge diffraction
The attenuation over rounded obstacles is usually higher than A_d in the above formula.
Approximate techniques to compute the diffraction loss over multiple knife edges have been proposed by
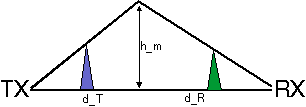
The method by Bullington defines a new `effective' obstacle at the point where the line-of-sight from the two antennas cross.
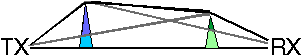
Epstein and Peterson suggested to draw lines-of-sight between relevant obstacles, and to add the diffraction losses at each obstacle.

Deygout suggested to search the `main' obstacle, i.e., the point with the highest value of v along the path. Diffraction losses over `secondary' obstacles are added to the diffraction loss over the main obstacle.
Many measurements of propagation losses for paths with combined diffraction and ground reflection losses indicate that knife edge type of obstacles significantly reduce ground wave losses. Blomquist suggested two methods to find the total loss:
![]()
and the empirical formula
![]()
where A_fs the free space loss, A_R the ground reflection loss and A_d the multiple knife-edge diffraction loss in dB values.