Multiple Access
Multiple Access methods address the problem of how many users can share the
same spectrum resources in an efficient manner. We distinguish between
- Multiple access within one cell, i.e., a fixed assignment of resources in time or bandwidth to specific users
- Random access, i.e., a dynamic assignment of spectrum resources in time or bandwidth to users, according to their needs
- Frequency reuse, i.e., assignment of spectrum resources considering the location of users and the attenuation of radio signals that travel over sufficiently large distances.
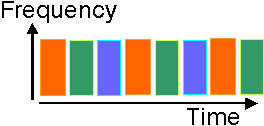
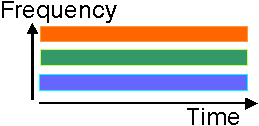
Examples of multiple access schemes are
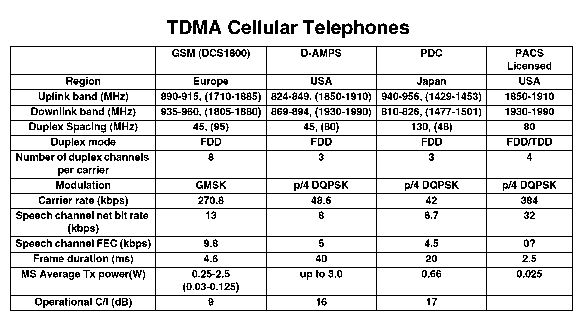
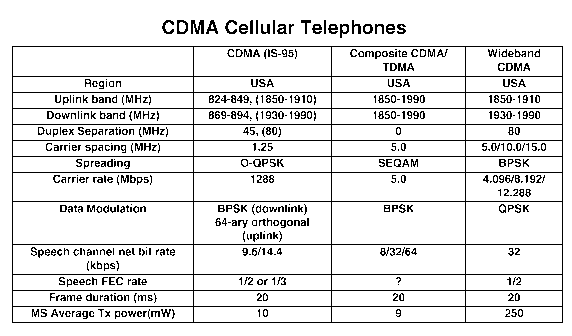
Modern cellular phone systems inherently use some form of FDMA, but on each
carrier multiple user signals are multiplexed. The latter involves TDMA (e.g.
GSM or D-AMPS),
CDMA (IS-95) or a combination
of both (UMTS).