
 |
JPL's Wireless Communication Reference WebsiteChapter: Network Concepts and Standards
|
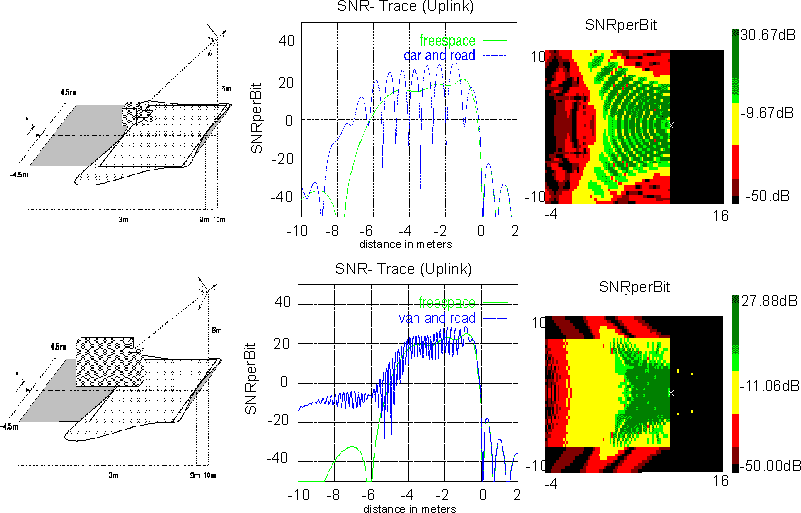
Figure 3: 5.8 GHz Channel characteristics
The DSRC channel is characterised by the dynamically changing influences of multi-path interference and shadowing as well as multi-access interference. To illustrate typical characteristics, the results of an analysis, which was carried out using an appropriate 5.8 GHz propagation modelling tool [13] are presented in figure 3.
A vehicle model was moved through a scenario such as depicted in figure 3. For the beacon antenna, a phased array antenna, which provides a shaped beam, was assumed. As a worst-case assumption an omni-directional vehicle antenna and horizontal polarisation was used. Analysing the results for the car model and comparing them with the results for free space propagation (see figure 3), a typical two-path characteristic with destructive and also constructive interference caused by the motor-hood can be observed. The results of the van model show reflections via the road surface. Using the car model, these reflections have been completely shadowed by the motor-hood. Again two-path propagation occurs, but due to the greater distance between reflector and receiver as well as the smaller reflectivity of the road surface, the fades are observed more frequently but with a smaller amplitude.
Note: As the DSRC standard for 5.8 GHz proposes circular polarisation, the impact of the motor-hood reflection can be reduced considerably.