
 Digital Audio Broadcasting
Digital Audio Broadcasting
DAB was standardized and developed in European Eureka EU-147 project, which started in
1988.
DAB tests started already in 1994, and the BBC started a network in 1995 followed soon
afterwards by Swedish and Danish operators. The BBC will cover 60% of the UK population in 1998.
Currently almost all European countries have operational or pre-operational services.
However, receiver sets have thus far not been widely available.
New services included improved "convenience", as there is no need to know the station's
wavelength'. DAB will provide more programmes, as it ensures a more efficient use of
spectrum. However, some critics say that initially it will only consume more spectrum
because programmes need to be provided both in analog and DAB formats. By exploiting
digital transmission and error correction techniques, the sound quality is much improved and
it guarantees 'static-free' reception and improved mobile reception. The goal of Eureka EU-147 was to achieve
"near CD" quality.
DAB is suitable for new (data) services. The listener can set voice / music power ratio and choose his own
dynamic range of the audio material. Along with the audio, additional information can be
transmitted, such as
- programme / format information
- song texts
- traffic information
- radio text
Digital transmission opens the possibility to have conditional access (subscriber radio)
DAB History
- During 1980s: development of theory of OFDM transmission, first tests
- 1994: first pilots
- Summer 1995: Pilot test with more than 12 transmitters in Germany
- September 1995: Regular BBC service in London
- 1996: Service in major urban areas in France
- Other pilots: Netherlands; Denmark; Sweden; Italy; Montreal (Canada).
Technical aspects of DAB
- Lower transmit power than analogue FM
- Bit synchronized transmitters allow Single Frequency Networks, that is, a program can
be disseminated by many transmitters which all operate on the same channel.
- DAB employs Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). This a type of Multi (Sub-) Carrier Modulation. This
modulation technique offers frequency diversity, and eliminates the effect of 'local' fades
- 15 to 20 programmes per carrier
- Bit rates:
- DAB can provide 2.3 Mbit/s with contiguous coverage, in 1.5 MHz bandwidth.
An effective bit rate of about 1.6 Mbit/s can contain up to 64 audio programs
- Source Coding
- MPEG audio encoding rates can range from 32 kbit/s to 384 kbit/s. The broadcaster can trade-off quality against number of programs.
MPEG-1 audio encoding is based on MUSICAM: "Mask pattern adapted Universal subband
Integrated Coding and Multiplexing", which exploits psycho-acoustic masking. Strong tones mask
nearby weak tones. Inaudible details are not transmitted.
- MPEG 1 video: 1.5 Mbit/s
- Data services in multiples of 8 kbit/s
- The transmit bandwidth is chosen much larger than the coherence bandwidth (at least 1.5 MHz)
- Problem to be researched: how to offer local radio coverage
| |
 |
Prototype DAB radio receiver by Philips Electronics.
|
 Exercise:
Exercise:
Explain why subcarrier interleaving for DAB and DTTB with multiple programs
preferably does not use a periodic interleaving scheme. Hint: consider the frequency transfer function
in a typical single frequency network with reception from two base stations.
DAB Service Parameters
Operating Modes
- Mode I: 200 MHz, carrier spacing 1 kHz, 2048 point FFT, transmit bandwidth about 1.536 MHz, guard interval is about 0.25 millisecond
- Mode II: 800 MHz, carrier spacing 4 kHz, 512 point FFT, transmit bandwidth about 1.536 MHz
- Mode III: 1500 MHz bandwidth, carrier spacing 8 kHz, 256 point FFT, transmit bandwidth about 1.536 MHz
Implementation
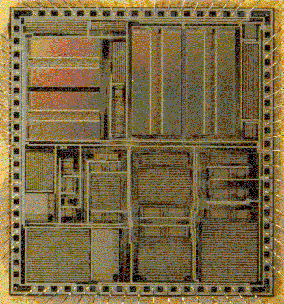
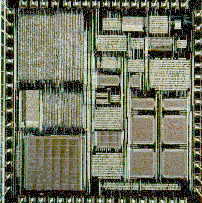
The European JESSI AE-14 DAB project aims at realization of chips for key components
of the DAB receiver.
| |
|
| |
|
Photo: DAB receiver chips FADIC 123 and SIVIC, developed by Philips. (courtesy: Jos Huisken, Group Digital VLSI, IC-Design Centre, Nat. Lab., Philips Research, Eindhoven)
|
- Synchronization to OFDM signal
- Demultiplexing
- 256, 512 or 2048 point FFT for OFDM demod.
- De-interleaving (requires about 0.5 to 1 Mbyte memory, depending on implementation)
- Viterbi Decoder







 Digital Audio Broadcasting
Digital Audio Broadcasting

