 |
www.WirelessCommunication.NLChapter: Wireless Channels
|
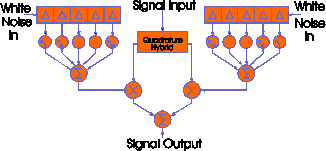
Figure: Block diagram of a narrowband Rayleigh fading simulator
(in baseband)
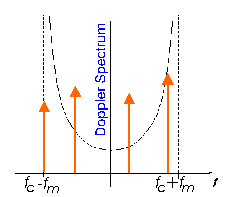
Figure: Crude approximation (orange) of the theoretical Doppler spectrum (Black)
used in animation taking only 4 components. (N=3)
N Frequency components are taken at
2 pi i
f_i = f_m cos -------- with i = 1, 2, .., N
2(2N+1)
with different amplitudes.
One component at the maximum Doppler shift is also added, but at
lesser amplitude.