
Measuring the Rician K Factor
The Rician K factor,
defined as the ratio of signal power in dominant component over the scattered, reflected power,
is a
very important in understanding the behavior of a short-range wireless channel.
It determines the distribution of the received signal amplitude.
Knowledge of the Rician K factor can be useful in determining the bit error rate of a channel among other useful metrics.
This K factor is very difficult difficult to directly, i.e., by physically
isolating the direct wave from the scattered components. However, the K-factor can be estimated from a set of different samples of the channels, for instance at different frequencies.
The method of matching first and second moments was used to determine the Rician K factor. This method sets the sample mean equal to the theoretical mean (both of the received signal amplitude). The following equation shows the theoretical mean of a Rician distributed random variable.
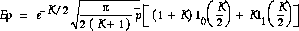
Regarding the second moment, the expectation of E[r^2] equals the local mean power,
composed of the power in the dominant component, plus the power is scattered components..
Since both the local mean power,  , and the sample mean, Er, can
be found empirically, this expression can be used to solve for K.
, and the sample mean, Er, can
be found empirically, this expression can be used to solve for K.
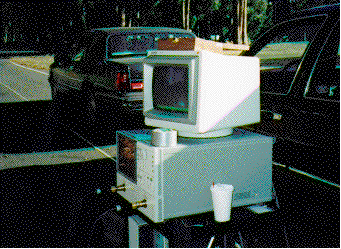
Figure: Network Analyzer used as Propagation Measurement Setup
 Audio
Audio
This method was used to evaluate for instance indoor channels at 2.4 GHz
and vehicle-to-vehicle channels.
Hear John Davis discuss how he measured wireless indoor and car-to-car channels.
- Audio: Meaurement Set-up and Statistical Procesing
The heart of the measurement set-up is a network analyzer. It samples the channel
at various frequencies. Channel impulse response are computed from this.
Using statistical processing on a PC, the r.m.s. delay spread
was computed.
Also, the Rician K-factor was computed from fluctuations seen in the frequency
transfer function.
- Audio: Resolution and Number of Samples
The network analyzer samples the frequency transfer function in a certain window.
- The width of the window determines the time resolution of the impulse response.
- The sampling distance determines aliasing of impulse response.





![]()
![]() , and the sample mean, Er, can
be found empirically, this expression can be used to solve for K.
, and the sample mean, Er, can
be found empirically, this expression can be used to solve for K.
 Audio
Audio