
Virtual Cellular Network (VCN)
A Virtual Cellular Network allow many terminals with
bursty traffic to access a fixed communications infrastructure,
using radio communication. All base stations listen to the same channel.
Terminals follow the slotted ALOHA
multiple access scheme.
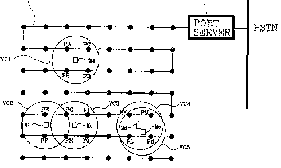
Figure: VCN architecture, with multiple receiving
ports all connected to a single port server.
A Virtual Cellular Network exploits site
diversity in the uplink:
a signal from a mobile terminal can be received at multiple base stations
simultaneously.
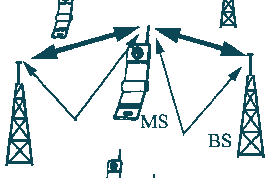
Capture Performance
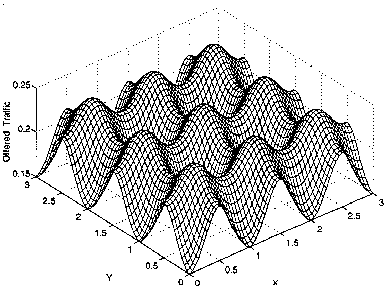
Traffic to be offered (transmission attempts per time slot per unit area)
versus terminal location (x,y). Spatially uniform throughput of 0.15
packet per slot per unit area. Base stations located at all
integer coordinates. Most retransmissions occur in areas relatively
far from base stations, but there we exploit site-diversity most.
Some References
- H.J. Kim and J.P. Linnartz, "Virtual Cellular Network, ...",
IEEE VTC Conference, Stockholm 1994.
- J.P.M.G. Linnartz, "Slotted ALOHA land-mobile
radio networks with site diversity", IEE
Proceedings I, Vol. 139, No. 1, Feb. 1992, pp.
58-70.
VCN Definition
A virtual cellular network uses a virtual cell
architecture, defined as an area of a predetermined size and
formed virtually around a mobile terminal during a period of time
the mobile terminal transmits one packet. The virtual cellular
network includes a plurality of ports connected to each other by
a port network for receiving uplink packets transmitted from the
mobile terminal, and a port server for selecting any one packet
among one or more duplicated packets from one or more ports
included within the virtual cell, transmitting the packet to a
destination, and transmitting downlink packets to the mobile
terminals.








