
 |
JPL's Wireless Communication Reference WebsiteChapter: Analog and Digital Transmission. Section: Digital Modulation, GMSK. |
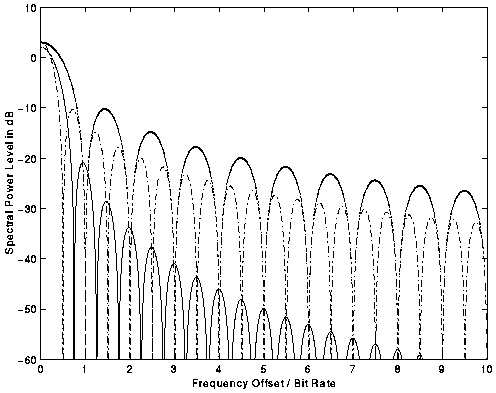
Figure: power density spectra
versus frequency normalized to user
bit rate.
| --- | Solid line: | GMSK | The GMSK spectrum has a somewhat wider main lobe than BPSK, but sidelobes are much weaker. This reduces adjacent channel interference. |
| ..... | BPSK | (The sinc-shaped spectrum) | |
| - . - . | QPSK | (The QPSK spectrum is half a wide as the BPSK spectrum) |
%-------------------------------------------
% matlab/spectra.m
% author: J.P. Linnartz
% created December, 1996
% This program computes power spectra of
% Several Digital Modulation Methods
%-------------------------------------------
pi = 3.141592;
sqrpi = pi2;
GMSK = [];
GBPSK = [];
GQPSK = [];
xaxis = [];
for i=1:1000
f = i/100;
% f is frequency normalized to to 1/(bit duration)
xaxis = [xaxis, f ];
ymsk = 16/sqrpi * (cos(6.2832 * f))2/ (1- 16 * f2)2;
GMSK = [GMSK, 10 * log10(ymsk)];
ybpsk = 2 * (sin(pi*f)/(pi*f))2;
GBPSK = [GBPSK, 10 * log10(ybpsk)];
yqpsk = 2 * (sin(2*pi* f)/(2*pi*f))2;
GQPSK = [GQPSK, 10 * log10(yqpsk)];
end
plot(xaxis,GMSK, 'y-',xaxis,GBPSK, 'c.',xaxis,GQPSK, 'c-.');
axis([0 10 -60 10]);
ylabel('Spectral Power Level in dB');
xlabel('Frequency Offset / Bit Rate');